Difference between revisions of "ECE 110/Spring 2018"
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
=== Test Reviews === | === Test Reviews === | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | * [[ECE_110/ | + | * [[ECE_110/Spring_2018/Test_1|Test 1]] |
| − | * [[ECE_110/ | + | * [[ECE_110/Spring_2018/Test_2|Test 2]] |
| − | -- | + | * Final: Test 1, Test 2, and Operational Amplifiers: |
| + | ** Know the Ideal Op-Amp assumptions (infinite internal input impedance, zero internal output impedance, and infinite internal voltage gain), | ||
| + | ** Know the implications when an Ideal Op-Amp is put into a circuit where the is feedback from the output to the inverting terminal (no voltage drop across the input terminals and no current into/out of the input terminals). | ||
| + | ** Know how to analyze Op-Amp circuits, generally by using KCL at the input terminals of the Op-Amp. | ||
| + | ** Understand that the only time you would write KCL at the output terminal of an Op-Amp is if you are trying to calculate the current coming out of the Op-Amp (which, incidentally, is general nonzero). | ||
| + | ** Understand that you cannot use KCL at ground if there is an Op-Amp circuit because we are not explicitly including several connections from ground that connect to the Op-Amp. See Figure 6.2-2 so see two additional connections to ground which we generally do not include while analyzing Op-Amp circuits but which would be required for using KCL at ground. | ||
| + | ** Example problems from the [http://classes.pratt.duke.edu/Gustafson/OmnibusTestBank.html Test Bank]: | ||
| + | *** EE 61 Spring 2001 Test 2 Problem 4 | ||
| + | *** EE 61 Fall 2001 Test 2 Problem 3 | ||
| + | *** ECE 110 Fall 2014 Test 2 Problem 5 | ||
| + | *** EGR 119(224) Spring 2009 Test 2 Problem 4 | ||
| + | *** EGR 224 Spring 2013 Test 2 Problem 4 (1) | ||
| + | *** EGR 224 Spring 2014 Test 2 Problem 4 (2) if the Z were all R instead | ||
| + | *** EGR 224 Spring 2016 Test 2 Problem 4 | ||
=== How do I get Dr. G's Files from Class? === | === How do I get Dr. G's Files from Class? === | ||
Latest revision as of 21:20, 29 April 2018
ECE 110 is a required course for all students planning to earn a major in Electrical and Computer Engineering or Biomedical Engineering at Duke University. It may also be taken to satisfy the cross-disciplinary requirement for the Civil and Environmental Engineering degree. This page is meant to provide answers to general questions about the course, not necessarily specific questions about content. There is also a Category:ECE 110 that will list all pages relevant to ECE 110. Note at the bottom of this page that it is a member of that category. This is the page for Spring, 2018.
Contents
Lab Supplemental Pages
Lab Errors
None yet!
Lab Supporting Documentation
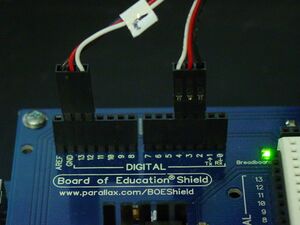
Connecting the Parallax Digital Trainer to the BOE Shield
This requires two male-to-male 3-header cables.
- The first cable will go from channels GND/13/12 on the BOE Shield to channels GND/P0/P1 on the PDT. The black wire should be on GND; for the BOE Shield, that is the second-to-leftmost pin on the top bus while for the PDT, that is the fourth pin from the top on the left of the socket.
- The second cable will go from channels 2/3/4 on the BOE Shield to P2/P3/P4 on the PDT. The black wire should be on pin 2 of the BOE Shield and in the sixth-from-the-bottom socket on the PDT. The white wire should be on pin 4 of the BOE Shield and in the fourth-from-the-bottom socket on the PDT.
Support Pages for Lecture Section 2 (Dr. G) for Spring 2018
Lecture / Homework Support Pages
Test Reviews
- Test 1
- Test 2
- Final: Test 1, Test 2, and Operational Amplifiers:
- Know the Ideal Op-Amp assumptions (infinite internal input impedance, zero internal output impedance, and infinite internal voltage gain),
- Know the implications when an Ideal Op-Amp is put into a circuit where the is feedback from the output to the inverting terminal (no voltage drop across the input terminals and no current into/out of the input terminals).
- Know how to analyze Op-Amp circuits, generally by using KCL at the input terminals of the Op-Amp.
- Understand that the only time you would write KCL at the output terminal of an Op-Amp is if you are trying to calculate the current coming out of the Op-Amp (which, incidentally, is general nonzero).
- Understand that you cannot use KCL at ground if there is an Op-Amp circuit because we are not explicitly including several connections from ground that connect to the Op-Amp. See Figure 6.2-2 so see two additional connections to ground which we generally do not include while analyzing Op-Amp circuits but which would be required for using KCL at ground.
- Example problems from the Test Bank:
- EE 61 Spring 2001 Test 2 Problem 4
- EE 61 Fall 2001 Test 2 Problem 3
- ECE 110 Fall 2014 Test 2 Problem 5
- EGR 119(224) Spring 2009 Test 2 Problem 4
- EGR 224 Spring 2013 Test 2 Problem 4 (1)
- EGR 224 Spring 2014 Test 2 Problem 4 (2) if the Z were all R instead
- EGR 224 Spring 2016 Test 2 Problem 4
How do I get Dr. G's Files from Class?
This is a work in progress - stay tuned!
F.A.Q.
- None as yet
Questions
Post your questions by editing the discussion page of this article. Edit the page, then scroll to the bottom and add a question by putting in the characters *{{Q}}, followed by your question and finally your signature (with four tildes, i.e. ~~~~). Using the {{Q}} will automatically put the page in the category of pages with questions - other editors hoping to help out can then go to that category page to see where the questions are. See the page for Template:Q for details and examples.
External Links
Note: there will be different homework assignments, and possibly different policies among the different sections -- be sure to follow the appropriate guidance for the appropriate section!
- http://classes.pratt.duke.edu/ECE110S18 - Dr. G's page for lecture
- https://piazza.com/duke/spring2018/ece110/home - Piazza page for Dr. G's lecture
- Sakai lab link - Sakai page for ECE 110L lab and common components
- Sakai class link - Sakai page for ECE 110L.002 lecture